

Anti hair loss therapy

Hair continuously experiences different stages of growth, including long-term (Anagen), degenerative period (Catagen), end-of-life (Telogen), and Exogen. The life cycle of each hair depends on the health of the hair follicle. Hair loss is divided into hair loss related to the growth phase of hair (e.g. hair loss during the rest period, hair loss at the beginning of growth) or hair loss (e.g., round baldness, scarred hair loss) involved in hair follicle inflammation. Pathological changes in hair itself directly affect the formation of hair, or indirectly affect hair due to a wide range of inflammatory problems throughout the scalp. Clinical treatment of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases may require immunosuppressants, antimalarial drugs, or other medications. Some inflammatory states can cause irreparable damage, so it is important to understand the basic concepts of hair pathology and avoid deterioration to irreversible hair loss.
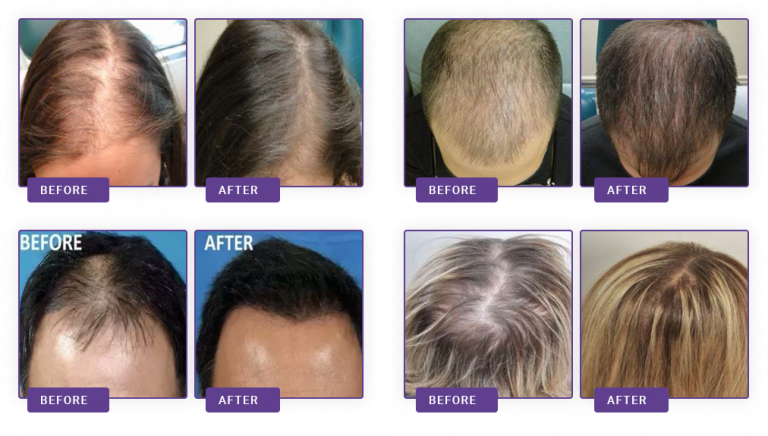
Generally speaking, the most common cause of hair loss is male baldness, which is estimated to affect up to 40% of women and 80% of men. Female male baldness is characterized by the retention of hair and the scalp of the pillow, and gradually thinning the hair and middle scalp. Male baldness affects the hair and frontal corners on both sides and may progress to complete baldness. Male baldness has proven to be effective treatments for minoxidil and finasteride. For female male baldness, ,finasteride and some other anti-androgens (e.g. spinorolactone) can be used in women with abnormal male hormones, and these girls tend to accompany other outward manifestations, such as oily skin, acne, hairy hair, and even congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
Natural regenerative drugs and blood growth molecules
Blood growth molecules help repair wound sydgin and tissue, especially tendons, ligaments, and muscles. Blood growth molecules are also commonly used in other clinical settings because platelets are considered to be a rich source of growth factors and other beneficial cytokines. Blood growth molecules are an effective way to treat hair loss because of their ability to rejuvenate hair and skin tissue. With regard to hair, blood growth molecules have shown positive results for hair growth in many clinical trials, in which it has been observed that it can reverse hair loss, promote hair growth and increase hair thickness.
What is a blood-growing molecule?
Blood growth molecules are defined as the extraction of plasma from high platelet concentrations in the body blood samples, usually greater than 1,000,000 platelets/uL; VWF, Tenth Factor), chemokines (e.g. leukocyte interleukin-8, beta-thrombogloglobulin, neutrophil hypertrophil activated, plateplate factor 4 platete), adhesion molecules (e.g. P-selectin P-selectin) and growth factors (e.g. platelet-derived growth factors transforming factor growth beta), vascular endothelial growth factor, matrix-derived growth factor 1 stromalaled growth factor 1 (CXCL 12), epidermal mal factor, fibroblast growth factor 7, beta-stemanic protein-derived-catenan. The clinical effect of blood growth molecules is based on the role played by these released molecules in the production of cell proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenic formation.
The role mechanism of blood growth molecules in hair loss
We know that many molecules are released when platelets are activated, including growth factors, which can play a role in cell growth (embryonic), regeneration, and angiogenesis. In various studies, these growth factors can act on stem cells in the hair follicle bulge region (bulge), promote the development of new hair follicles and promote vascular rebirth. There are two types of cells that affect hair follicle regeneration:
1. The outer embryo layer stem cells are located in the bulge area of the hair follicles and can be further differentiated into epidermal cells and sebum glands.
2. Germinative cells (germinative cells) from interstitial sources are found in dermal papilla.
In addition to the interactions with different growth factors released by platelets, the interactions between the two cell groups are thought to activate the growth period of hair (proliferative phase) and therefore produce new follicle units (follive units).
The growth of dermal nipples is achieved by promoting fibroblast growth factor-7 (fibroblast growth gactor 7), βbeta-serial protein(beta-catenin), βextracellular signal-related hormone (ERK) and Aktsignalsignal. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) helps hair growth-related angiogenesis and affects the growth of dermal structures. Mysenchyme shows the plasticity associated with hair-and-hair period, which helps with the regulation of hair follicles (transformation) for example, the regulation of male baldness from hairvellus to permanent hair terminal, which regulates the reversal of hair follicles is important for male baldness treatment. In addition, blood growth molecules also improve the blood supply of hair follicles, and the vascular structure around the hair follicles is increased after treatment with blood growth molecules.
Therefore, the growth factor released by the blood growth molecule from the activated platelets promotes the growth, differentiation and rebirth of hair follicles. In addition, they improve blood vessel formation and blood supply around hair follicle tissue. Blood-growing molecules also extend hair growth (anagen) and have an anti-apoptosis effect.